EVOM™ – The Proven Gold Standard for TEER Measurement

EVOM™ – The Proven Gold Standard for TEER Measurement
Synopsis
World Precision Instruments (WPI) has manufactured TEER instrumentation, including the EVOM, EVOMX, EVOM2, EVOM3, EVOM™ Manual, and Millicell® ERS-2 (a WPI OEM product), for over 3 decades. Millipore’s Millicell® ERS 3.0 recently became available and is NOT manufactured by WPI, nor has it any published evidence that supports its accuracy, precision or application of TEER measurement Users are cautioned to ensure their TEER measurements are taken using a WPI manufactured and validated product, like EVOM™ Manual, the proven gold standard for TEER measurement, to ensure accuracy and reproducibility.

Figure 1: WPI-manufactured TEER Instruments.
TEER Meter Comparison Chart
EVOM™ Technology Powered TEER Measurement in Research
In the realm of biomedical research and clinical applications, the choice of equipment and technology plays a critical role in the accuracy and reliability of data collection. Two tools commonly used today for measuring trans-epithelial electrical resistance (TEER) in cell culture systems are the EVOM2 and Millicell® ERS-2, both manufactured by WPI, using the TEER technology that was invented by WPI and patented in 19901 (Figure 1). Since 2008, WPI has been the Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) of Millipore’s Millicell® ERS-2, producing this TEER instrument, and allowing Millipore to rebrand it. WPI was responsible for not only discovering and enabling this TEER technology, but also was responsible for the production, quality control, validation, supply, and second-level support of the Millicell® ERS-2.
Together, EVOM2 and Millicell® ERS-2 have been featured in thousands of peer reviewed publications, demonstrating the accurate, reproducible and meaningful data that these instruments produce. In fact, since 1990, there have been 4,507 publications that mention “transepithelial electrical resistance,” with 72.1% (3,250) of those publications specifically citing WPI’s instrumentation2-4 (Figure 2). TEER, enabled by WPI’s technology, is now globally recognized as a reliable and validated measurement for the resistance across a cell layer and a critical parameter in cell biology, tissue engineering, drug delivery, and barrier function studies. TEER has now been applied to thousands of impactful studies utilizing this measurement to evaluate biological barrier functionality, assess drug permeability, develop and validate disease models, optimize cell culture conditions, and performing toxicity assessments.
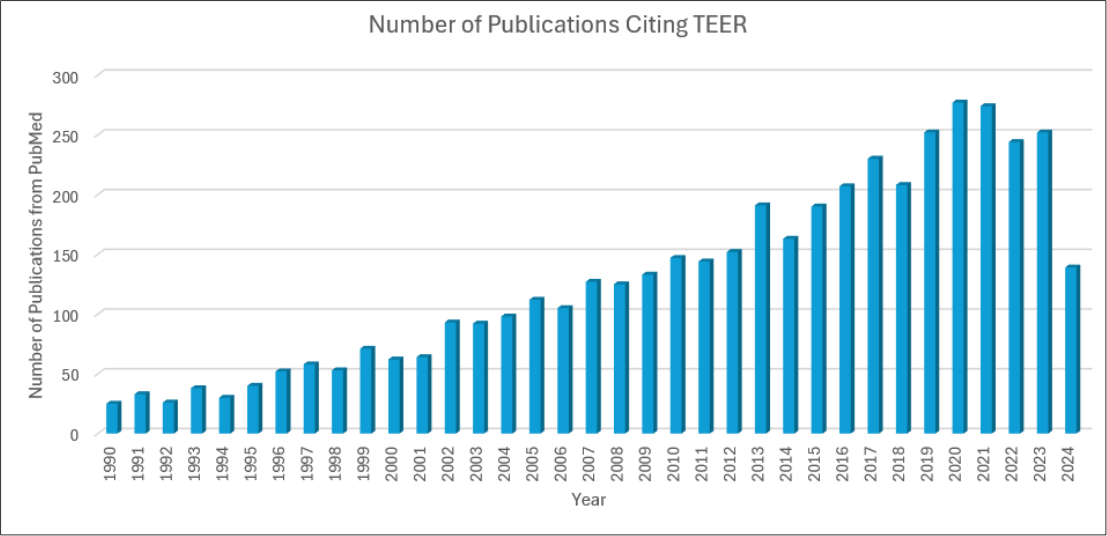
Figure 2: Number of Publications Citing “Transepithelial Electrical Resistance” on https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ from 1990- July 11, 2024. A total of 4,507 publications have cited TEER with the number of publications growing over time since the invention of TEER in 1991.
Data from New EVOM™ Meters Compatible with Legacy Meters
In 2018, WPI continued its tradition of improving and optimizing technology with a goal of adding features and functionalities to its instruments, while maintaining the integrity and precision of the data that is collected using its instruments, by launching the EVOM3, later re-branded as the EVOM™ Manual, in 20225 (Figure 1). The EVOM™ Manual features several improvements over the EVOM2 and Millicell® ERS-2, including automatic data logging, a low noise design that improves accuracy and resolution, automatically performs a 20X sample average to improve precision and stability, and continuous data logging directly onto a PC. Most importantly, the EVOM™ Manual uses the same underlying TEER technology as the EVOM2 and Millicell® ERS-2 and is compatible with these legacy meters. This means that when researchers upgrade their instrument from an EVOM2 or Millicell® ERS-2 to an EVOM™ Manual, there is reliability and continuity in the data (Figure 3). By maintaining consistency in the method of WPI’s TEER measurement, established experimental models and assays do not have to be replicated and re-validated in order to compare data that is collected from these instruments, saving researchers significant time and resources in the transition from EVOM2 or Millicell® ERS-2 to EVOM™ Manual.
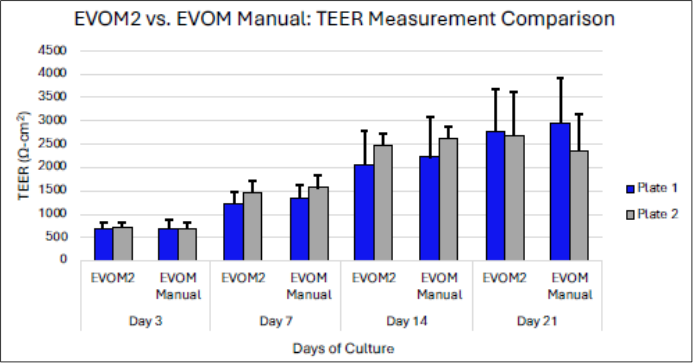
Figure 3: TEER readings are not statistically different from the EVOM2 and the EVOM™ Manual. While the EVOM™ Manual is more user-friendly and can measure a 24-well plate in 25% of the time it takes using EVOM2, the TEER readings are not statistically different between the EVOM2 and EVOM™ Manual.
ERS 3.0 Does NOT Utilize EVOM™ Technology
In 2024, Millipore launched a new product, the Millicell® ERS 3.0, which was not developed or manufactured by WPI. While both the EVOM™ Manual and Millicell® ERS 3.0 devices serve a similar purpose, they differ significantly in terms of their proven reliability. While the EVOM™ Manual uses the TEER technology that has been the subject of thousands of peer-reviewed publications for nearly 35 years, the Millicell® ERS 3.0 has not had a peer-reviewed publication to date, and there is a stark lack of data publicly available for this instrument. No studies have been published that demonstrate that the data that is collected using the Millicell® ERS 3.0 is even relatively close to the value that of the WPI manufactured legacy TEER instruments, including Millicell® ERS-2, despite having a similar name. Not only does the Millicell® ERS 3.0 lack validation and verification, but it also has significant changes that may impact the data that is obtained from it. For example, none of the EVOM™ Manual or Millicell® ERS-2 legacy electrodes are compatible with the Millicell® ERS 3.0. Instead, researchers are required to purchase a new electrode made using gold, which has electrical properties that vary significantly from Ag/AgCl that was used in the EVOM™ and ERS-2.
Trust the EVOM™ Brand with its Proven History
WPI has been a trusted name in the industry for decades, providing researchers with high-quality instruments and equipment. The EVOM™ technology and its associated instruments, including the EVOM2, the Millicell® ERS-2, and the EVOM™ Manual, are well-established devices that have stood the test of time, utilizing the same electrodes and underlying TEER technology to collect data consistently and accurately. Researchers value the reliability and consistency of data obtained from the EVOM™ Manual thanks to WPI's years of experience and expertise in the field. On the other hand, the Millipore Millicell® ERS 3.0 is a new entrant in the market, with no publicly available data, raising significant concerns regarding proof of its accuracy and reliability. Unlike the EVOM™ Manual, the Millicell® ERS 3.0 is a system that is unvalidated for most of the applications that researchers will utilize TEER for. The scientific community values peer reviewed publications that require rigorous testing and verification for accuracy. This could raise equal concern in the minds of researchers about the data collected from the Millicell® ERS 3.0 and its suitability for critical research applications. Further, the inability to seamlessly continue experiments and studies means that it will take a significant amount of time and resources for a laboratory to implement the Millicell® ERS 3.0 into their workflows in the way that can be done with the EVOM™ Manual.
In conclusion, when it comes to choosing between the WPI EVOM™ Manual and the Millipore Millicell® ERS 3.0 for TEER measurements, researchers must consider the value of decades of experience and proven technology offered by WPI. The reliability and consistency of data obtained from the EVOM™ Manual make it a trusted choice for researchers who prioritize accuracy and precision in their work. On the other hand, the change in manufacturing and unvalidated nature of the Millicell® ERS 3.0 raises concerns about the reliability of data collected from this system, casting a shadow of doubt on its effectiveness and suitability for critical research applications. Researchers are encouraged to weigh these factors carefully when selecting the appropriate equipment for their research needs.
References
- United States Patent Application: US4912060A. “Method and apparatus for electrical testing of membranes”
- Pubmed, National Library of Medicine: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
- Bioz: https://www.bioz.com/
- WPI Publications: https://www.wpiinc.com/scientific-publications
- EVOMTM Manual: https://www.wpiinc.com/evm-mt-03-01-EVOMTM tm-manual-for-teer-measurement.html